

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Covalent Binding method of immobilisation
المؤلف:
John M Walker and Ralph Rapley
المصدر:
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 5th Edition
الجزء والصفحة:
8-1-2021
2426
Covalent Binding method of immobilisation
This method of immobilisation involves the formation of a covalent bond between a biocatalyst and support material . The bond is normally formed between functional groups present on the surface of a support material and functional groups on amino acid residues on the surface of an enzyme. A number of amino acid functional groups are suitable for participation in covalent bond formation. Those most often involved are the amino group (NH2) of lysine or arginine, the carboxyl group (CO2H) of aspartic acid or glutamic acid, the hydroxyl group (OH) of serine or threonine and threshold group (SH) of cysteine.
Many varied support materials are available for covalent binding and the extensive range of supports available reflects the fact that there is no ideal support material . Therefore, the advantages and disadvantages of a given support are taken into account when considering possible procedures for a given biocatalyst immobilisation. Many factors may influence the selection of a particular support and research has shown that hydrophilicity (water attraction) is the most important factor for maintaining enzyme activity in a support material environment. Consequently, polysaccharide polymers, which are very hydrophilic, are popular support materials for enzyme immobilisation.
For example, cellulose, dextran, starch and agarose are often used for enzyme immobilisation. The sugar residues in these polymers contain hydroxyl (OH) groups that are suitable for chemical activation to provide covalent bond formation (Figure 1). The OH groups also form hydrogen bonds with water molecules and thereby create a hydrophilic environment within a support material.
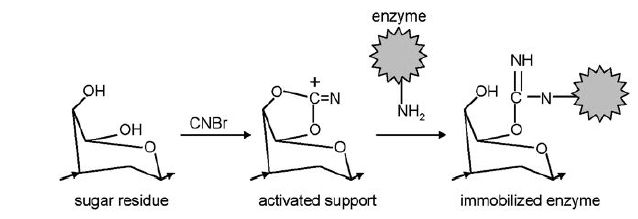
Figure 1. Covalent immobilisation by activation of a carbohydrate support material with CNBr and coupling of an enzyme (via free amino group) to the activated support to form an isourea bond.
Polysaccharide supports do have a weakness in that they are susceptible to microbial/fungal disintegration and organic solvents used in some reaction processes can cause shrinkage of polysaccharide gels.
Support materials are usually used in bead form and there are many procedures for coupling an enzyme and a support in a covalent bond. However, most reactions fall into the following main categories:
- formation of an isourea linkage;
- formation of a diazo linkage;
- formation of a peptide bond;
- an alkylation reaction.
It is important to choose a reaction method that will not inactivate an enzyme by reacting with amino acid residues at the enzyme active site. Hence if an enzyme employs a carboxyl group at its active site for participation in catalysis, then it is wise to choose a reaction method that involves amino groups for covalent bond formation with a support.Basically two steps are involved in covalent binding of enzymes to support materials.
First, functional groups on a support material are activated by a specific chemical reagent such as cyanogen bromide (CNBr), and second, an enzyme is added in a coupling reaction to form a covalent bond with the activated support material. Normally an activation reaction is designed to make functional groups on a support strongly electrophilic (electron deficient). In the coupling reaction, these groups will react with strong nucleophiles (electron donating), such as the amino (NH2) functional groups of certain amino acids on the surface of an enzyme, to form a covalent bond. It is possible to vary the coupling conditions to allow single-point or multiple-point attachment and influence the stability of an immobilised enzyme .
In the CNBr method, an enzyme and support are joined via an isourea linkage. In carbodiimide activation, a support material should have a carboxyl (CO2H) functional group and an enzyme and support are joined via a peptide bond. If the support material contains an aromatic amino functional group, it can be diazotised using nitrous acid. Subsequent addition of enzyme leads to the formation of a diazo linkage between a reactive diazo group on a support and the ring structure of an aromatic amino acid such as tyrosine.
It is important to recognise that no method of immobilisation is restricted to a particular type of support material and that an extremely large number of permutations are possible between methods of immobilisation and support materials. This is possible by chemical modification of normal functional groups on a support material to produce a range of derivatives containing different functional groups. For example, the normal functional group in cellulose is the OH of glucose and chemical modifications of these groups have produced a range of cellulose derivatives such as AE-cellulose (aminoethyl), CM-cellulose (carboxymethyl) and DEAE-cellulose (diethylaminoethyl). Thus chemical modification increases the range of immobilisation methods that can be used for a given support material.
 الاكثر قراءة في الانزيمات
الاكثر قراءة في الانزيمات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















