

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography 2
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
22-4-2020
2317
Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography
The addition of a new species to the running buffer will separate the molecules in the initial sample. This separation can occur based on the molecules’ affinities for the added species. For example, uncharged, nonpolar molecules can attract to neutral species, while charged species can attract to added ionic species. There are several different ways to perform this experiment based on the properties of the added species. The addition of cyclodextrins (or micelles) to the running buffer allows the separation of chiral species. This is described as MEKC, or Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography. This technique can separate compounds (which had similar mobilities in CZE experiments) due to the difference in affinities of the sample molecules for detergent micelles.
Neutral species will partition between the running buffer and the hydrophobic interior of the micelles. The micelles, which are negatively charged, have a retention time greater than the EOF. Thus, as molecules enter the micelles they are slowed down. The stronger an affinity the neutral species has for the micelle, the longer its retention time. The more nonpolar neutral species have the highest affinity for the micelles. Charged particles that have hydrophobic groups will also be retained by interaction with the hydrophobic core of the micelle. Highly positively charged particles will interact with the surface of the micelle and also be retained. These interactions can be seen in Figure 6.6. You can see that the separation of the species in the mixture will be changed by the addition of detergent to the running buffer. You can tailor your separation to exactly suit your needs by experimenting with different additions to the running buffer.
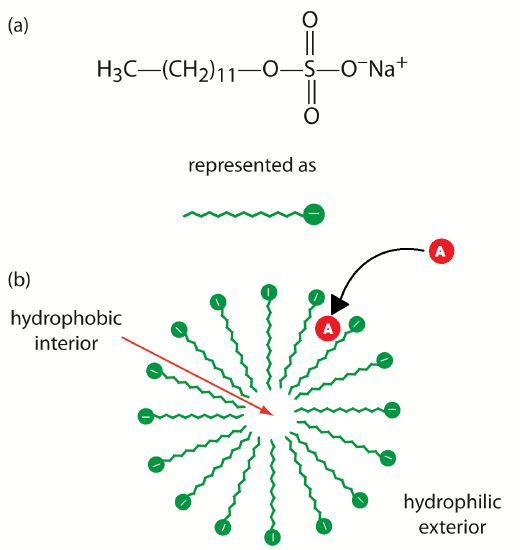
Figure 6.6: Micellular Interactions within the Capillary. (a) Structure of sodium dodecylsulfate and its representation, and (b) cross-section through a micelle showing its hydrophobic interior and its hydrophilic exterior. The cross-section shows the migration of neutral compound “A” into the hydrophobic interior. The vep of “A” can be retarded due to the partitioning into the micelle.
 الاكثر قراءة في التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)
الاكثر قراءة في التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















