

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
GC: Column Oven
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
4-2-2020
1491
GC: Column Oven
The thermostatted oven serves to control the temperature of the column within a few tenths of a degree to conduct precise work. The oven can be operated in two manners: isothermal programming or temperature programming. In isothermal programming, the temperature of the column is held constant throughout the entire separation. The optimum column temperature for isothermal operation is about the middle point of the boiling range of the sample. However, isothermal programming works best only if the boiling point range of the sample is narrow. If a low isothermal column temperature is used with a wide boiling point range, the low boiling fractions are well resolved but the high boiling fractions are slow to elute with extensive band broadening. If the temperature is increased closer to the boiling points of the higher boiling components, the higher boiling components elute as sharp peaks but the lower boiling components elute so quickly there is no separation.
In the temperature programming method, the column temperature is either increased continuously or in steps as the separation progresses. This method is well suited to separating a mixture with a broad boiling point range. The analysis begins at a low temperature to resolve the low boiling components and increases during the separation to resolve the less volatile, high boiling components of the sample. Rates of 5-7 °C/minute are typical for temperature programming separations.
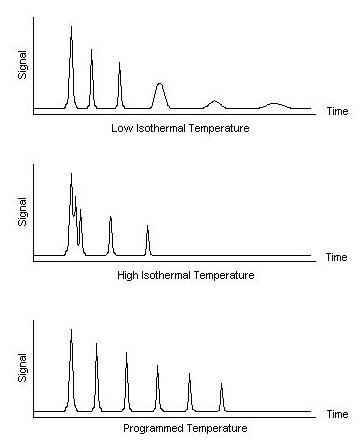
Figure 1. The effect of column temperature on the shape of the peaks.
 الاكثر قراءة في التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)
الاكثر قراءة في التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















