

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
27-8-2018
1942
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance
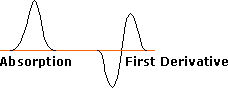
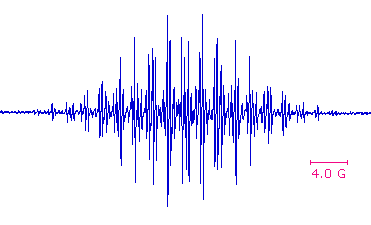
The same unpaired or odd electron that renders most radical intermediates unstable and highly reactive may be induced to leave a characteristic "calling card" by a magnetic resonance phenomenon called "electron spin resonance" (esr) or "electron paramagnetic resonance" (epr). Just as a proton (spin = 1/2) will occupy one of two energy states in a strong external magnetic field, giving rise to nmr spectroscopy; an electron (spin = 1/2) may also assume two energy states in an external field. Because the magnetic moment of an electron is roughly a thousand times larger than that of a proton, the energy difference between the spin states falls in the microwave region of the spectrum (assuming a moderate magnetic field strength). The lifetime of electron spin states is much shorter than nuclear spin states, so esr absorptions are much broader than nmr signals. One way of improving the signal to noise ratio in esr spectra is to display them as first derivatives rather than absorptions. These displays are illustrated on the left below. In practice, esr spectra may be quite complex, as shown by the derivative spectrum of triphenylmethyl radical on the right. This complexity is the result of hyperfine splitting of the resonance signal by protons and other nuclear spins, an interaction similar to spin-spin splitting in nmr spectroscopy. For example, the esr signal from methyl radicals, generated by x-radiation of solid methyl iodide at -200º C, is a 1:3:3:1 quartet (predicted by the n + 1 rule). The magnitude of signal splitting is much larger than nmr coupling constants (MHz rather than Hz), and is usually reported in units of gauss. The complexity of the triphenylmethyl spectrum is due to three different hyperfine splittings: 3 para hydrogens, 6 ortho hydrogens & 6 meta hydrogens. Ideally this should produce 196 lines, but imperfect resolution reduces the number observed.
|
ESR Signal Types |
|
|---|
 الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















