

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Quantum Mechanics and the Hydrogen Atom
المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
المصدر:
College Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 51
3-7-2017
811
Quantum Mechanics and the Hydrogen Atom
Quantum mechanics began with a daring hypothesis by Louis de Broglie (he was a student at the time): if light has a dualistic wave/particle nature, why not matter? His reasoning led to the prediction that a particle of mass m and velocity u would exhibit wavelike properties with wavelength
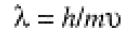 (1.1)
(1.1)
Thus for an electron beam with u = 1.46 × 106 m/s, Eq. (1.1) gives λ = 5.0 Å, comparable to the ionic spacing in a crystal. In 1920, it was found that a crystal would indeed diffract an electron beam, and de Broglie's crazy idea was proven!
Once it was established that electrons could behave like waves, physicists began looking for ways of dealing with electrons using their wavelike properties, and in 1926, Schrödinger found the solution. Schrödinger's wave equation does not attempt to calculate the trajectory of an electron nor does it make any assumptionsa bout planetary orbits of electrons about nuclei. Rather it computes a wave function, the square of which is the probability density of finding an electron at some point in space. When applied to the hydrogen atom, the results are similar to those of Bohr, with the following equation for the allowed energies:
 (1.2)
(1.2)
where µ is the reduced mass, µ = memn/(me + mn) » me (me and mn, are the masses of the electron and the nucleus), e is the electronic charge, Z is the nuclear charge in units of |e| (Z = 1 for H, 2 for He+), eo = 8.854 × 10-12 C2J-1m-1 is the permittivity of free space, h is Planck's constant, and n is a positive integer. The energy of the photon emitted from an excited H atom is the difference between allowed energies:
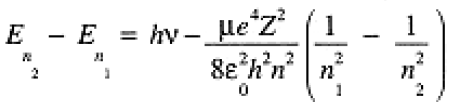 (1.3)
(1.3)
In agreement with Eq. (1.4)
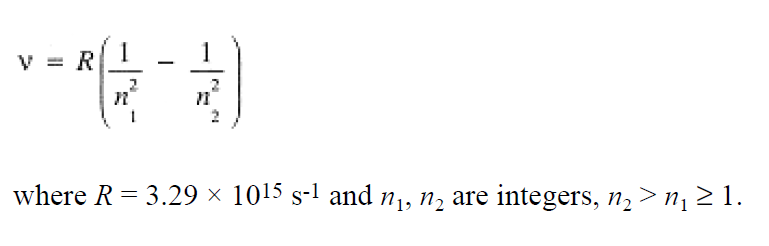 (1.4)
(1.4)
The integer n in Eq. (1.2), called the principal quantum number, determines the energy levels in a one electron atom or ion and largely determines the average distance of the electron from the nucleus. A complete description of the H atom requires two additional quantum numbers:
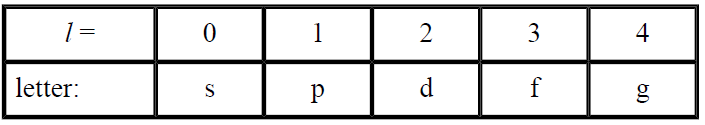
The angular momentum quantum number, l, defines the shape of the electronic distribution, called an orbital. l may have any integral value between 0 and n - 1. Chemists often use a letter to represent the numerical value of l:
The magnetic quantum number, m, describes the orientation of orbitals in space. m may have any integral value between -l and +l.
Thus for l = 0, m = 0, for l = 1, m = ± 1, 0; in general there are 2l + 1 values of m.
The shapes of the s, p, and d orbitals are shown in Figure 1.1.

Figure 1.1.: Shapes of s, p, and d-orbitals.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء الكم
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء الكم
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















