
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Jansky’s Experiment
المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
الجزء والصفحة:
p 3
24-2-2016
1991
Jansky’s Experiment
As often happens in science, RF radiation from outer space was first discovered while someone was looking for something else. Karl G. Jansky (1905-1950) worked as a radio engineer at the Bell Telephone Laboratories in Holmdel, New Jersey. In 1931, he was assigned to study radio frequency interference from thunderstorms in order to help Bell design an antenna that would minimize static when beaming radio-telephone signals across the ocean. He built an awkward looking contraption that looked more like a wooden merry-go-round than like any modern-day antenna, much less a radio telescope. It was tuned to respond to radiation at a wavelength of 14.6 meters and rotated in a complete circle on old Ford tires every 20 minutes. The antenna was connected to a receiver and the antenna’s output was recorded on a strip-chart recorder.
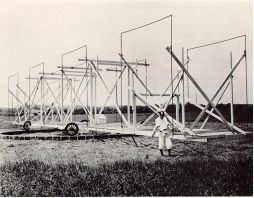
Jansky’s Antenna that First Detected Extraterrestrial RF Radiation
He was able to attribute some of the static (a term used by radio engineers for noise produced by unmodulated RF radiation) to thunderstorms nearby and some of it to thunderstorms farther away, but some of it he couldn’t place. He called it “ . . . a steady hiss type static of unknown origin.”
As his antenna rotated, he found that the direction from which this unknown static originated changed gradually, going through almost a complete circle in 24 hours. No astronomer himself, it took him a while to surmise that the static must be of extraterrestrial origin, since it seemed to be correlated with the rotation of Earth.
He at first thought the source was the sun. However, he observed that the radiation peaked about 4 minutes earlier each day. He knew that Earth, in one complete orbit around the sun, necessarily makes one more revolution on its axis with respect to the sun than the approximately 365 revolutions Earth has made about its own axis. Thus, with respect to the stars, a year is actually one day longer than the number of sunrises or sunsets observed on Earth. So, the rotation period of Earth with respect to the stars (known to astronomers as a sidereal day) is about 4 minutes shorter than a solar day (the rotation period of Earth with respect to the sun). Jansky therefore concluded that the source of this radiation must be much farther away than the sun. With further investigation, he identified the source as the Milky Way and, in 1933, published his findings.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















