

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The helium atom: two electrons
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p16
11-2-2016
2395
Many-electron atoms
The helium atom: two electrons
The preceding sections have been devoted to hydrogen-like species containing one electron, the energy of which depends only on n (equation 1.1); the atomic spectra of such species contain only a few lines associated with changes in the value of n (Figure 1).
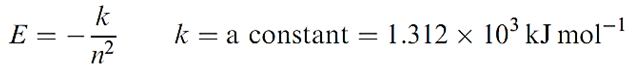 (1.1)
(1.1)
It is only for such species that the Schrodinger equation has been solved exactly. The next simplest atom is He (Z = 2), and for its two electrons, three electrostatic interactions must be considered:
* attraction between electron (1) and the nucleus;
* attraction between electron (2) and the nucleus;
* repulsion between electrons (1) and (2).
The net interaction will determine the energy of the system.
In the ground state of the He atom, two electrons with ms = 1/2 and -1/2 occupy the 1s atomic orbital, i.e. the electronic configuration is 1s2. For all atoms except hydrogen- like species, orbitals of the same principal quantum number but differing Ɩ are not degenerate. If one of the 1s2 electrons is promoted to an orbital with n = 2, the energy of the system depends upon whether the electron goes into a 2s or 2p atomic orbital, because each situation gives rise to different electrostatic interactions involving the two electrons and the nucleus. However, there is no energy distinction among the three different 2p atomic orbitals. If promotion is to an orbital with n = 3, different amounts of energy are needed depending upon whether 3s, 3p or 3d orbitals are involved, although there is no energy difference among the three 3p atomic orbitals, or among the five 3d atomic orbitals. The emission spectrum of He arises as the electrons fall back to lower energy states or to the ground state and it follows that the spectrum contains more lines than that of atomic H.
In terms of obtaining wave functions and energies for the atomic orbitals of He, it has not been possible to solve the Schrodinger equation exactly and only approximate solutions are available. For atoms containing more than two electrons, it is even more difficult to obtain accurate solutions to the wave equation.
In a multi-electron atom, orbitals with the same value of n but different values of Ɩ are not degenerate.
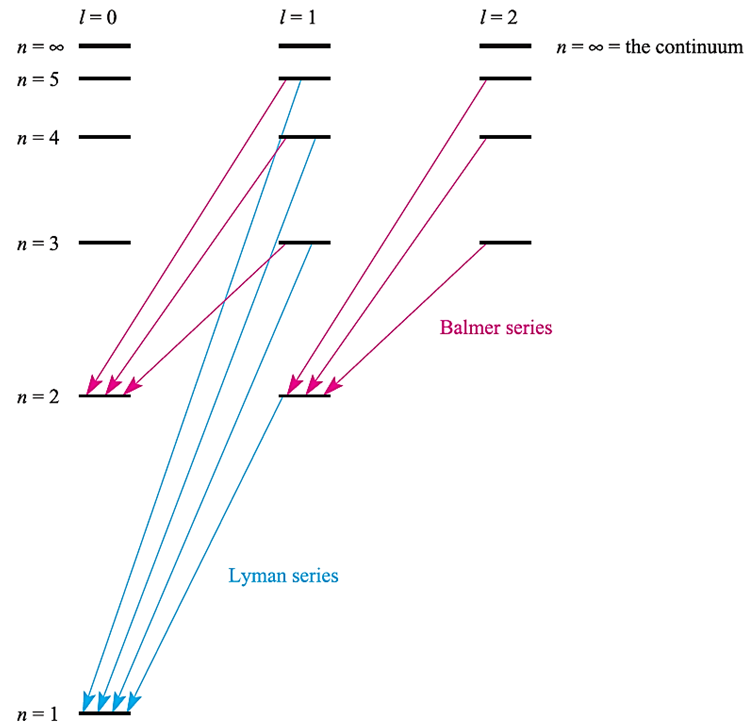
Fig. 1 Some of the transitions that make up the Lyman and Balmer series in the emission spectrum of atomic hydrogen.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















