
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)
 المؤلف:
James Carton
المؤلف:
James Carton
 المصدر:
Oxford Handbook of Clinical Pathology 2024
المصدر:
Oxford Handbook of Clinical Pathology 2024
 الجزء والصفحة:
3rd edition , p70-71
الجزء والصفحة:
3rd edition , p70-71
 2025-01-20
2025-01-20
 724
724
Definition
• An idiopathic interstitial pneumonia limited to the lung and associated with a histological appearance of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP).
Epidemiology
• the majority of patients are between 50 and 70y.
• Men are affected about twice as often as women.
• Cigarette smoking increases the risk by several fold.
Aetiology
• Unknown but currently thought that recurrent exposure to environmental irritants leads to repetitive episodes of alveolar injury and an abnormal repair mechanism.
Pathogenesis
• Injured alveolar epithelial cells in susceptible individuals react by overexpressing profibrotic cytokines, such as transforming growth factor- beta and interleukin- 10, which stimulate irreversible lung scarring (Fig. 1).
Presentation
• Progressive breathlessness and non- productive cough.
Macroscopy
• Marked lung fibrosis with honeycomb change.
• Disease most marked at the peripheries of the lower lobes.
Histopathology
• Heterogeneous, non- uniform fibrotic process, characterized by markedly scarred areas of the lung juxtaposed to islands of relatively normal lung (‘spatial variability’).
• evidence of active ongoing fibrosis in the form of numerous fibroblastic foci (‘temporal variability’).
* this histopathological picture, known as UIP, is always seen in IPF but is not specific for it.
Prognosis
• Very poor, with average survival of only 2– 3 years from diagnosis.
• A common terminal event is an acute exacerbation of IPF, characterized histologically by diffuse alveolar damage on a background of the UIP histological pattern
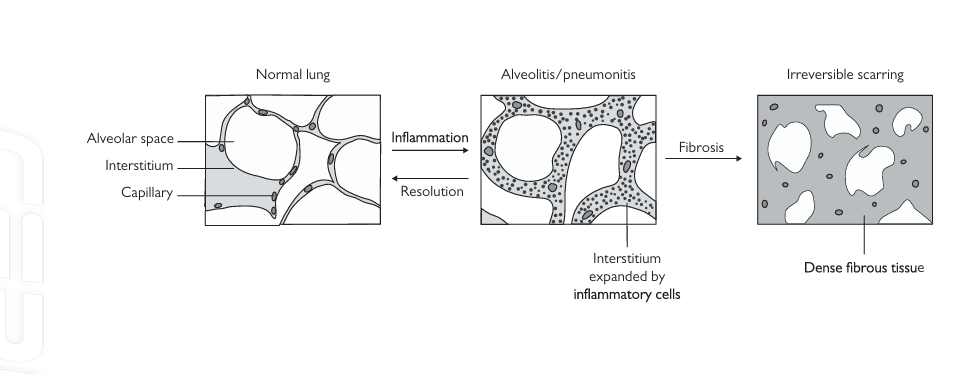
Fig.1 evolution of diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD). the normal interstitium is thin and contains pulmonary artery capillaries. In DPLD, the interstitium becomes expanded by an inflammatory cell infiltrate (‘pneumonitis’ or ‘alveolitis’), impairing gas exchange. Complete resolution can occur, but the danger is the development of fibrosis which permanently destroys the lung parenchyma. Reproduced with permission from Clinical Pathology (Oxford Core texts), Carton, James, Daly, Richard, and Ramani, Pramila, Oxford University Press (2006), p. 126, Figure 7.10.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


