
Chromatin Architecture Dynamics of the IgH Locus in V(D)J Recombination, CSR, and SHM
 المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
 المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 30-4-2021
30-4-2021
 2129
2129
Chromatin Architecture Dynamics of the IgH Locus in V(D)J Recombination, CSR, and SHM
KEY CONCEPTS
- Chromatin architecture of the Ig locus facilitates V(D)J recombination and class switch recombination (CSR).
- CTCF binds to multiple sites over the IgH locus and mediates long-range genomic interactions.
- Activation-induced deaminase (AID) targets are predominantly grouped within super-enhancers and regulatory clusters.
During B and T cell development, the coding elements for BCR and TCR are assembled from widely dispersed gene segments. Antigen receptor loci contain multiple V, D, and/or J and C coding elements, and the assembly of these antigen receptors is controlled at multiple levels, including chromatin architecture, nuclear location, and epigenetic marking. This will bring into close proximity elements that are separated by about 2.5 Mb for their recombination (FIGURE 1). The Ig H and L chain loci and TCR loci are not simple linear chromosomal structures but possess a three-dimensional configuration, which orchestrates DNA recombination at these loci. Indeed, the IgH chain locus tends to fold into a comprehensive pattern of loop arrangements that shorten the distances between gene segments and allow longrange genomic interactions to occur at relatively high frequencies to facilitate V(D)J recombination.
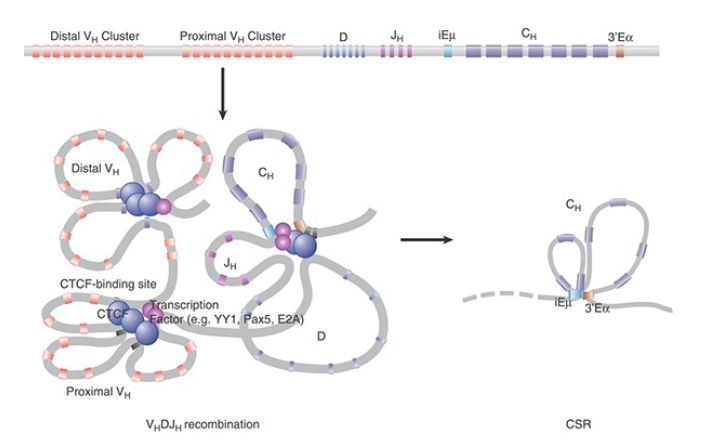
FIGURE 1.Chromatin architecture of Ig locus facilitates V(D)J recombination and CSR. CTCF, which is important for implementing chromatin conformation, modulates V(D)J recombination by regulating enhancer-promoter interaction and locus compaction. Iem:3’Ea interactions create long-range chromatin interactions directed by the Ih promoters and Igh enhancers, which create spatial proximity between Sm and downstream S region loci and facilitates recombination between the broken S regions and creates a matrix of chromatin contacts.
Left panel is modified from Figure 5 of Ong and Corces (2014) Nat. Rev. Gent. 15:234–246.
The DNA-binding zinc finger nuclear protein CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) mediates long-range chromatin looping and is important for implementing chromatin conformation. CTCF may modulate V(D)J recombination by regulating locus compaction and promoter–enhancer interactions, thereby influencing the spatial conformation of the IgH locus and antisense transcription. This generates noncoding RNAs that can further shape the chromatin architecture.
The Ig, and possibly TCR, alleles are sequestered at the transcriptionally repressive nuclear lamina in lymphoid progenitor cells. Before the pro-B cell stage, the IgH locus is released from the lamina to associate with the transcription and/or recombination machineries. Committed pro-B cells undergo broad chromatin conformational changes, in which chromatin looping of CTCFbinding sites at the IgH locus occurs independently of the iEμ enhancer and contributes to the compaction of the locus. Two CTCF- binding sites within the intergenic control region 1
(IGCR1), located between the VH and DH clusters, mediate ordered and lineage-specific VH -DJH recombination and bias distal over proximal VH rearrangements. IGCR1 suppresses the transcriptional activity and the rearrangement of proximal VH segments by forming a CTCF-mediated loop that presumably isolates the proximal VH promoter from the influence of the downstream iEμ enhancer. Likewise, before pro-B cell stages, CTCF promotes distal over proximal VK rearrangement by blocking the communication between specific enhancer and promoter elements in the Igκ locus.
The formation of the S-S synapsis, which is essential for CSR, is mediated by long-range intrachromosomal interactions between distantly located IgH transcriptional elements. This threedimensional chromatin architecture simultaneously brings I promoters into close proximity with iEμ and 3′Eα enhancers to facilitate transcription. Transcription across S-region DNA leads to RNA polymerase II accumulation that promotes the introduction of activating chromatin modifications and hyperaccessible chromatin to ensure AID activity. In mature resting B cells, the iEμ and 3′Eα enhancers are in close spatial proximity by forming a chromatin loop. B cell activation leads to cytokine-dependent enrollment of the I promoters to the iEμ–3′Eα complex and allows transcription of S regions targeted for CSR, likely facilitated by a three-dimensional structure adopted by the IgH locus.
Although AID specifically targets the Ig locus, it also acts with muchlower efficiency on a limited number of non-Ig genes (off-targets), leading to mutations and translocations that contribute to B cell tumorigenesis. AID targets, however, are not randomly distributed across the genome, but rather predominantly associated with topologically complex and highly transcribed super-enhancers and regulatory clusters. These include multiple interconnected transcriptional regulatory elements and strong convergent transcription, in which normal-sense transcription of the gene overlaps with super-enhancer–derived antisense enhancer RNA (eRNA) transcription. AID deaminates active promoters and eRNA enhancers that are interconnected in some instances over megabases of linear chromatin. This would provide a critical step toward recombination of widely spread V(D)J regions.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


