Kepler's Second Law
Kepler's second law relates the speed of the planet to the area swept out by a line connecting the sun to the planet. If we think of the sun as being at the origin of the coordinate system, then the line from the sun to the planet is what we have been calling the coordinate vector 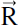 . It is also called the radius vector
. It is also called the radius vector 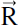 . Kepler's second law explicitly states that the radius vector
. Kepler's second law explicitly states that the radius vector 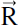 sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
To apply Kepler's second law to the output of our Orbit 1 program, we note that we had the computer plot a cross at equal times along the orbit. Thus the area swept out by the radius vector should be the same as 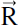 moves from one cross to the next. To check this prediction, we
moves from one cross to the next. To check this prediction, we
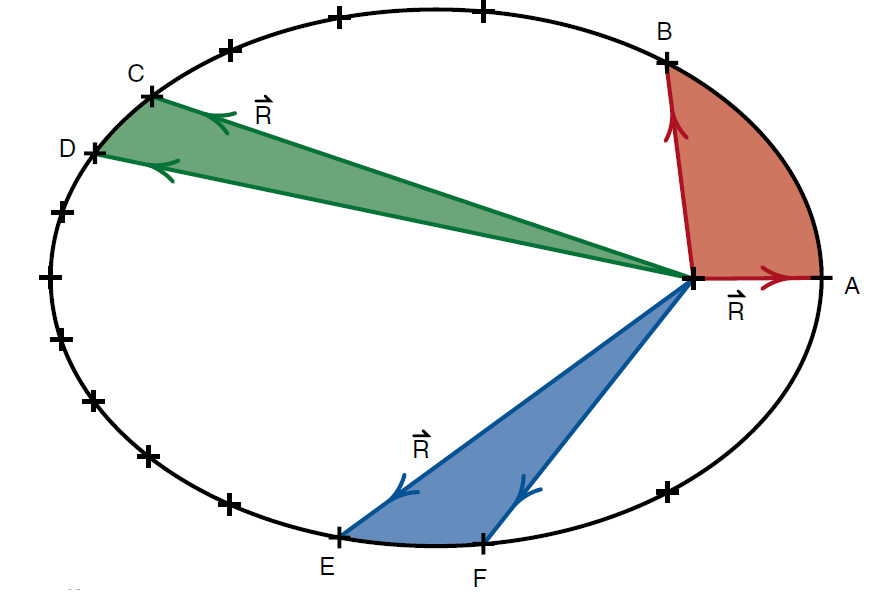
Figure 1: Kepler’s Second Law. The radius vectorR should sweep out equal areas in equal time.
have in Figure (30) reproduced the output, shaded the areas swept out as R moves from positions A to B, from C to D, and from E to F. These areas should look approximately equal; you will check that they are in fact equal.
The most significant consequence of Kepler's second law is that in order to sweep out equal areas while the radius vector is changing length, the planet or satellite must move more rapidly when the radius vector is short, and more slowly when the radius vector is long. The planet moves more rapidly when in close to the sun, and more slowly when far away.
An extreme example of elliptical satellite orbits are the orbits of some of the comets that periodically visit the sun. Halley's comet, for example, visits the sun once every 76 years. The comet spends about 1 year in the close vicinity of the sun, where it is visible from the earth, and the other 75 years on the rest of its orbit which goes out beyond the edge of the planetary system. The comet moves rapidly past the sun, and spends the majority of the 76 year orbital period creeping around the back side of its orbit where its radius vector is very long.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


