

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Crystal structure disorders: disorders involving F and O atoms
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 406
23-2-2018
2011
Crystal structure disorders: disorders involving F and O atoms
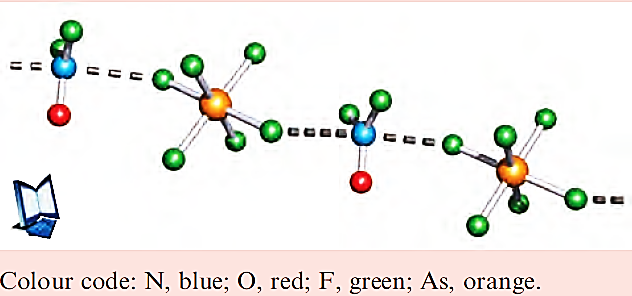
Not all structure solutions are straightforward. Some involve disordering of atomic positions, a problem that, for example, made the elucidation of the structure of C60 difficult. Examples of disordered structures occur commonly in oxofluorides because the O and F atoms are similar in size and possess similar electronic properties. Thus, in a crystal containing molecules of an oxofluoride XFxOy, a given atomic position might be occupied by O in one molecule and by F in another molecule. The overall result is modelled by fractional occupation of each site by O and F. Fractional occupancies can lead to difficulties in determining true X_F and X_O bond lengths and true bond angles. The compound [F2NO][AsF6]- represents a classic example of the problem. Although first prepared and characterized
in 1969, its structure was not reported until 2001. The [F2NO] ions in crystalline [F2NO][AsF6] are disordered such that the fluorine occupancy of each ‘F’ position is 78% and 77% respectively (rather than being 100%), and the fluorine occupancy of the ‘O’ position is 45% (rather than being 0%). The paper cited in the further reading below illustrates how the structural data can be treated so that meaningful N_O and N_F bond lengths and F_N_F and F_N_O bond angles are obtained. Crystalline [F2NO][AsF6] is composed of infinite chains of alternating cations and anions. There are close contacts between the N atom of each cation and the F atoms of adjacent [AsF6]- ions as shown in the figure.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















