
Lewis Electron-Dot Structures
 المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
 المصدر:
College Chemistry
المصدر:
College Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 60
الجزء والصفحة:
p 60
 6-7-2017
6-7-2017
 2236
2236
Lewis Electron-Dot Structures
The first great advance in qualitative understanding of chemical bonding was G. N. Lewis's suggestion in 1916 that atoms in stable molecules or ions tend to attain the configuration of the nearest noble gas.
For elements on the right side of the periodic table, this means acquiring eight valence electrons, the octet rule. Thus when Na and Cl atoms react to form NaCl, Na loses an electron to attain the Ne configuration and Cl gains an electron to attain the Ar configuration:

When a covalent bond is formed, the atoms share an electron pair, often obeying the octet rule by sharing electron pairs. For example, C achieves an octet in CH4 by sharing each of its 4 valence electrons with a H atom, which contributes 1 electron. Similarly N, with 5 valence electrons, achieves an octet in NH3 by sharing 3 electrons with H atoms, leaving an unshared pair; O, with 6 valence electrons, achieves an octet in H2O by sharing 2 electrons with H atoms, leaving two unshared pairs.
These structures are shown in Figure 8-1, where the shared electron pair is represented by a line between the bonded atoms. Polyatomic ions like NH4+ and OH- also have structures obeying the octet rule. Notice that in the structures of Figure below, H has a share of two electrons, which is as expected if it is to attain the He configuration; we might say that H obeys the doublet rule. Similar reasoning applied to covalently bonded transition metals allows an expansion beyond eight electrons.
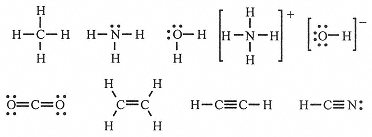
Figure 8-1.
Lewis electron-dot structures.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


