

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The effects of temperature on μeff
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 583
22-2-2017
1318
The effects of temperature on μeff
So far, we have ignored the effects of temperature on μeff. If a complex obeys the Curie Law (equation 1.2), then μeff is independent of temperature; this follows from a combination of equations 1.1 and 1.2.
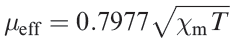 (1.1)
(1.1)
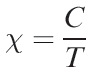 (1.2)
(1.2)
where C = Curie constant; T = temperature in K. However, the Curie Law is rarely obeyed and so it is essential to state the temperature at which a value of μeff has been measured. For second and third row d-block metal ions in particular, quoting only a room temperature value of μeff is usually meaningless; when spin–orbit coupling is large, μeffis highly dependent on T.
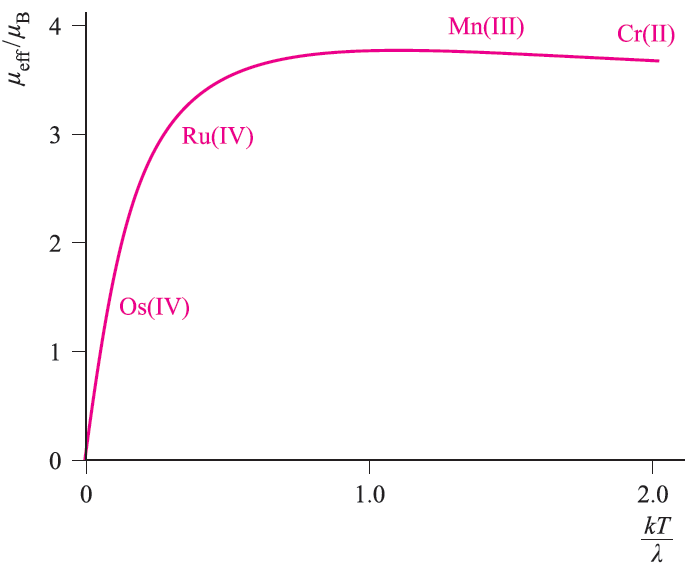
Fig. 1.1 Kotani plot for a t2g4 configuration; λ is the spin– orbit coupling constant. Typical values of μeff(298 K) for Cr(II), Mn(III), Ru(IV) and Os(IV) are indicated on the curve.
For a given electronic configuration, the influence of temperature on μeffcan be seen from a Kotani plot of μeff against kT/λ where k is the Boltzmann constant, T is the temperature in K, and λ is the spin–orbit coupling constant. Remember that λ is small for first row metal ions, is large for a second row metal ion, and is even larger for a third row ion. Figure 1.1 shows a Kotani plot for a t2g4 configuration; four points are indicated on the curve and correspond to typical values of μeff(298 K) for complexes of Cr(II) and Mn(III) from the first row, and Ru(IV) and Os(IV) from the second and third rows respectively. Points to note from these data are:
- since the points corresponding to μeff(298 K) for the first row metal ions lie on the near-horizontal part of the curve, changing the temperature has little effect on μeff;
- since the points relating to μeff(298 K) for the heavier metal ions lie on parts of the curve with steep gradients, μeff is sensitive to changes in temperature; this is especially true for Os(IV).
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















