
Pressure, Temperature and RMS Speed
 المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
 المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 230
الجزء والصفحة:
p 230
 1-1-2017
1-1-2017
 1944
1944
Pressure, Temperature and RMS Speed
Now consider our first kinetic theory problem. Imagine a gas, consisting of n moles being confined to a cubical box of volume V. ''What is the connection between the pressure p exerted by the gas on the walls and the speeds of the molecules?" Pressure is defined as Force divided by Area or 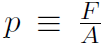 where
where 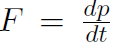 . Using Newtonian Mechanics, shows that
. Using Newtonian Mechanics, shows that
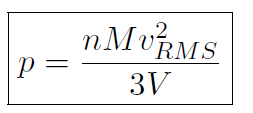
where n is the number of moles, M is the mass of 1 mole of the gas (so that nM is the total mass of the gas), vRMS is the average speed of the molecules and V is the volume of the gas. The above equation is derived purely from applying Newtonian mechanics to the individual molecules. Now by comparing to the ideal gas law pV = nRT or 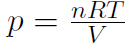 we must have
we must have 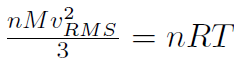 or
or
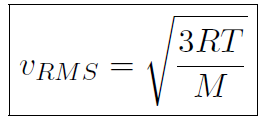
which shows that the temperature T is related to the speed of molecules!
As shown the speed of molecules at room temperature is very large; about 500 m/sec for air (about 1000 mph).
 الاكثر قراءة في الفيزياء الكيميائية
الاكثر قراءة في الفيزياء الكيميائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


