
Special Cases of 1st Law of Thermodynamics
 المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
 المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 221
الجزء والصفحة:
p 221
 30-12-2016
30-12-2016
 2556
2556
Special Cases of 1st Law of Thermodynamics
1. Adiabatic Processes
Adiabatic processes are those that occur so rapidly that there is no transfer of heat between the system and its environment. Thus Q = 0 and
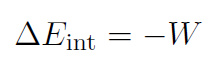
For example if we push in the piston very quickly then our work will increase the internal energy of the gas. It will store potential energy (ΔU = ΔEint) like a spring and make the piston bounce back when we let it go.
2. Constant-volume Processes
If we glue the piston so that it won't move then obviously the volume is constant, and 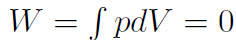 , because the piston can't move. Thus
, because the piston can't move. Thus
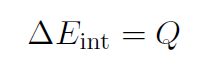
which means the only way to increase the internal energy of the gas is by adding heat Q.
3. Cyclical Processes
Recall the motion of a spring. It is a cyclical process in which the spring oscillates back and forth. After one complete cycle the potential energy U of the spring has not changed, thus ¢U = 0. Similarly we can push in the piston, then let it go and it will push back to where it started, similar to the spring. Thus ΔEint = 0 and
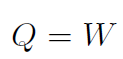
meaning that work done equals heat gained.
4. Free Expansion
Another way to get ΔEint = 0 is for
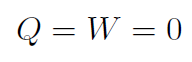
 الاكثر قراءة في الديناميكا الحرارية
الاكثر قراءة في الديناميكا الحرارية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


