
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Refraction
المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
الجزء والصفحة:
p35
28-2-2016
2079
Refraction
Refraction is the deflection or bending of electromagnetic waves when they pass from one kind of transparent medium into another. The index of refraction is the ratio of the speed of electromagnetic energy in a vacuum to the speed of electromagnetic energy in the observed medium. The law of refraction states that electromagnetic waves passing from one medium into another (of a differing index of refraction) will be bent in their direction of travel.
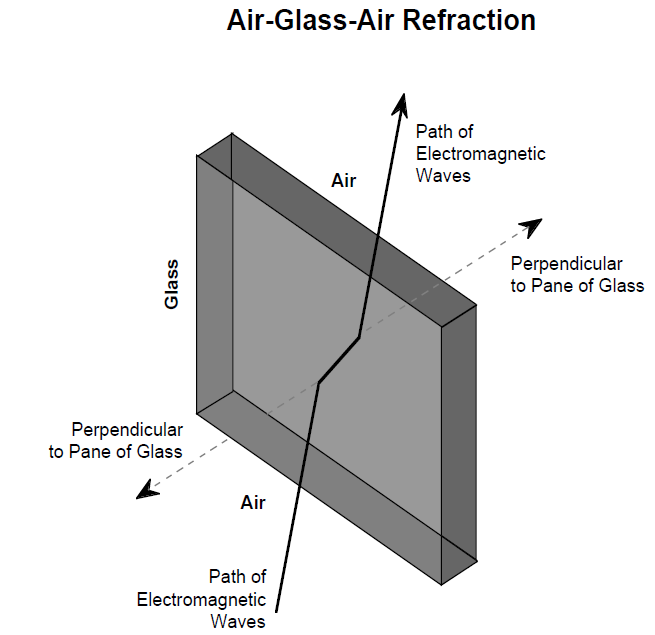
Usually, substances of higher densities have higher indices of refraction. The index of refraction of a vacuum, by definition, is 1.0. The index of refraction of air is 1.00029, water is 1.3, glass about 1.5, and diamonds 2.4. Since air and glass have different indices of refraction, the path of electromagnetic waves moving from air to glass at an angle will be bent toward the perpendicular as they travel into the glass. Likewise, the path will be bent to the same extent away from the perpendicular when they exit the other side of glass.
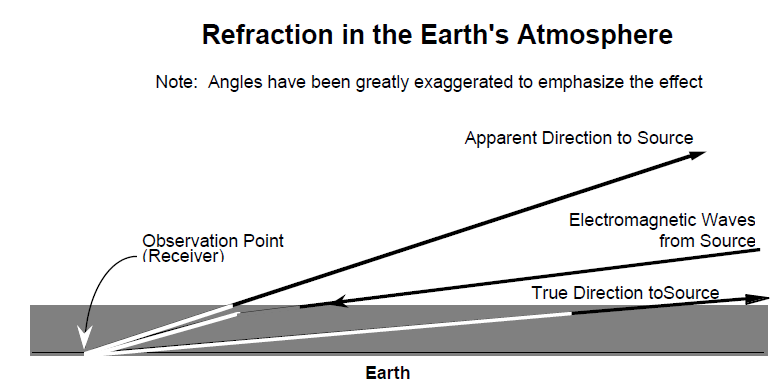
In a similar manner, electromagnetic waves entering Earth's atmosphere from space are slightly bent by refraction. Atmospheric refraction is greatest for radiation from sources near the horizon (below about 15° elevation) and causes the apparent altitude of the source to be higher than the true height. As Earth rotates and the object gains altitude, the refraction effect decreases, becoming zero at zenith (directly overhead). Refraction's effect on sunlight adds about 5 minutes to the daylight at equatorial latitudes, since the sun appears higher in the sky than it actually is.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















