
Faraday Rotation
 المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
 المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
p41
الجزء والصفحة:
p41
 25-2-2016
25-2-2016
 1865
1865
Faraday Rotation
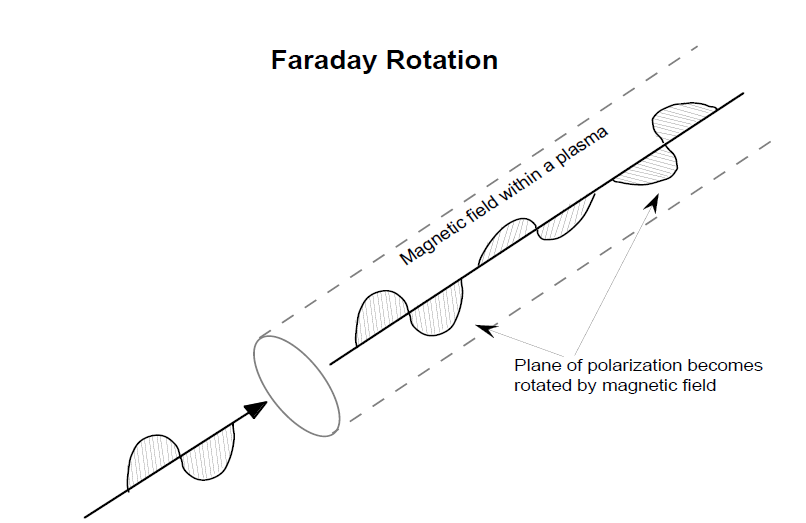
Faraday rotation (or Faraday effect) is a rotating of the plane of polarization of the linearly polarized electromagnetic waves as they pass through a magnetic field in a plasma. A linearly polarized wave may be thought of as the sum of two circularly polarized waves of opposite hand. That is, one wave is polarized to the right and one wave is polarized to the left. (Both waves are at the same frequency.) When the linearly polarized wave passes through a magnetic field, the right polarized wave component travels very slightly faster than the left polarized wave component. Over a distance, this phenomenon has the effect of rotating the plane of the linearly polarized wave. A measure of the amount of rotation can give a value of the density of a plasma.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


