
Arrays, Matrices
 المؤلف:
W.D. Wallis
المؤلف:
W.D. Wallis
 المصدر:
Mathematics in the Real World
المصدر:
Mathematics in the Real World
 الجزء والصفحة:
12-13
الجزء والصفحة:
12-13
 2-2-2016
2-2-2016
 2013
2013
Suppose a movie theater sells three types of tickets—Adult (A), Student (S), and Child (C). The theater charges more after 6 PM, so tickets may also be classified as Day (D) or Evening (E). If 43 Adult, 33 Student and 18 Child tickets are sold for the afternoon session, and 78 Adult, 45 Student and 12 Child tickets are sold in the evening, the day’s ticket sales could be represented by the following table:

An array of data like this is called a rectangular array, a two-dimensional array or simply an array. An array consisting only of numbers is called a matrix. In our example, the actual numbers are given by the matrix
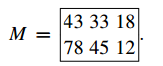
We shall usually denote matrices by single upper-case letters. In general, matrices can be used whenever the data is classified in two ways; in the example, the classifications are ticket types (A, S, C) and session times (D, E). The horizontal layers are called rows and the vertical ones columns for example, the first row in the above matrix M is

and the second column is

If a matrix has p rows and q columns, we refer to it as a “p by q matrix” or say “the matrix is p×q.” The numbers p and q are the dimensions of the matrix.
Sample Problem 1.1 A furniture manufacturer makes tables and chairs. In January he made 200 tables and 850 chairs; in February, 300 tables and 1,440 chairs; in March, 140 tables and 880 chairs. Represent these data in an array.
Solution. Write T for tables, C for chairs.

It is possible that a matrix can have only one row or only one column. A matrix with one of its dimensions equal to 1 is called a vector. An m×1 matrix is a column vector of length m, while a 1×n matrix is a row vector of length n. The individual rows and columns of a matrix are vectors, which we call the row vectors and column vectors of the matrix.
The element in the i-th row and j-th column of a matrix is called the (i, j) entry and it is denoted by the subscript i j; for example, a matrix M has (i, j) entry mi j.
Similarly, the i-th entry of a vector is denoted by subscript i.
It is possible for arrays to have more than two dimensions.
 الاكثر قراءة في المصفوفات و نظريتها
الاكثر قراءة في المصفوفات و نظريتها
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


