

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The temperature-dependence of reaction enthalpies
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins، Julio de Paula
المصدر:
ATKINS PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
ص56-57
2025-11-03
261
The temperature-dependence of reaction enthalpies
The standard enthalpies of many important reactions have been measured at different temperatures. However, in the absence of this information, standard reaction enthalpies at different temperatures may be calculated from heat capacities and the reaction enthalpy at some other temperature (Fig. 2.19). In many cases heat capacity data are more accurate that reaction enthalpies so, providing the information is avail-able, the procedure we are about to describe is more accurate that a direct measure ment of a reaction enthalpy at an elevated temperature. It follows from eqn 2.23a that, when a substance is heated from T1 to T2, its enthalpy changes from H(T1) to
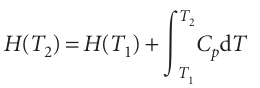
(We have assumed that no phase transition takes place in the temperature range of interest.) Because this equation applies to each substance in the reaction, the standard reaction enthalpy changes from ∆rHo(T1) to
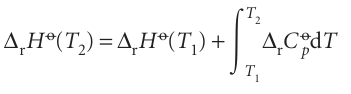
where ∆rCpo is the difference of the molar heat capacities of products and reactants under standard conditions weighted by the stoichiometric coefficients that appear in the chemical equation:
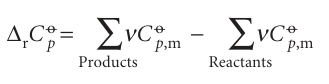
Equation 2.36 is known as Kirchhoff’s law. It is normally a good approximation to assume that ∆rCp is independent of the temperature, at least over reasonably limited ranges, as illustrated in the following example. Although the individual heat capacities may vary, their difference varies less significantly. In some cases the temperature dependence of heat capacities is taken into account by using eqn 2.25.
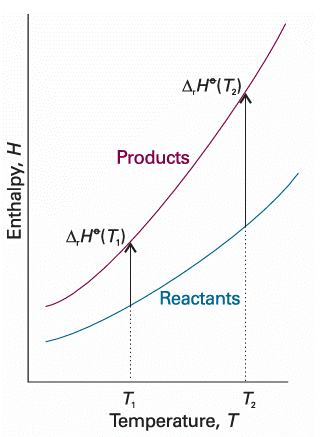
Fig. 2.19 An illustration of the content of Kirchhoff’s law. When the temperature is increased, the enthalpy of the products and the reactants both increase, but may do so to different extents. In each case, the change in enthalpy depends on the heat capacities of the substances. The change in reaction enthalpy reflects the difference in the changes of the enthalpies.

 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















