
Effect on the Lattice Parameter
 المؤلف:
C. Br´ echignac P. Houdy M. Lahmani
المؤلف:
C. Br´ echignac P. Houdy M. Lahmani
 المصدر:
Nanomaterials and Nanochemistry
المصدر:
Nanomaterials and Nanochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
p4
الجزء والصفحة:
p4
 2-12-2015
2-12-2015
 1554
1554
Effect on the Lattice Parameter
Let us now consider the effects of the increase in the surface-to-volume ratio as the object size decreases. To do this, we consider first the very simple case of a liquid sphere of diameter 2R. Due to the curvature of the surface, a pressure is generated toward the inside of the sphere. The excess pressure ΔP inside the sphere, in the purely hydrostatic case, is given by the Laplace equation
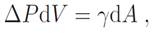 (1)
(1)
where dV is the volume change corresponding to a change dA in the area of the droplet. In the case of a sphere, (above) takes the form
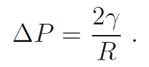 (2)
(2)
For a spherical solid, the specific surface energy must be replaced by the surface stress tensor gij . To simplify the problem, consider the case of a solid with simple cubic structure. In this case, γ is isotropic and we have
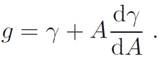 (3)
(3)
Moreover, we may recall the definition of the compressibility, viz.,
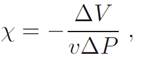 (4)
(4)
where v is the atomic volume of the solid, which can also be defined as a3, where a is the lattice parameter. Combining (1) and (4), We obtain the relative variation of the lattice parameter:
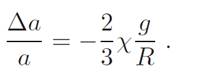
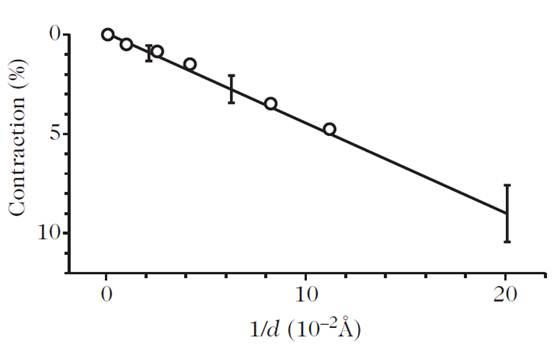
Fig. 1. Contraction of the lattice parameter of copper clusters as a function of the reciprocal of their diameter. Circles correspond to measurements of electron energy loss near an ionisation threshold (SEELFS). Taken from De Crescenzi et al. [1]. The straight line shows measurements of X-ray absorption (EXAFS). Taken from Apai et al. [2]
We thus find that there is a contraction of the crystal lattice due to the pressure exerted toward the interior of the particle. This contraction is proportional to the surface stress and inversely proportional to the particle size.
The lattice contraction in nanometric particles has been observed on many occasions. Figure 1 shows the change in lattice parameter for copper clusters, measured by the electron energy loss technique known as SEELFS andalso by X-ray absorption near an ionisation threshold (see below).
References
1. M. De Crescenzi, M. Diociaiuti, L. Lozzi, P. Picozzi, S. Santucci: Phys. Rev. B35, 5997 (1987)
2. G. Apai, J.F. Hamilton, J. St¨ohr, A. Thomson: Phys. Rev. Lett.43, 165 (1979)
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء النانو
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء النانو
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


