

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
The Lambda Repressor and Its Operators Define the Immunity Region
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
الجزء والصفحة:
7-6-2021
1983
The Lambda Repressor and Its Operators Define the Immunity Region
KEY CONCEPTS
- Several lambdoid phages have different immunity regions.
- A lysogenic phage confers immunity to further infection by any other phage with the same immunity region.
The presence of lambda repressor explains the phenomenon of immunity. If a second lambda phage DNA enters a lysogenic cell, repressor protein synthesized from the resident prophage genome will immediately bind to OL and OR in the new genome. This prevents the second phage from entering the lytic cycle.
The operators were originally identified as the targets for repressor action by virulent mutations (λvir). These mutations prevent the repressor from binding at OLor OR , with the result that the phage inevitably proceeds into the lytic pathway when it infects a new host bacterium. Note that λvir mutants can grow on lysogens because the virulent mutations in OL and OR allow the incoming phage to ignore the resident repressor and thus enter the lyticcy cle. Virulent mutations in phages are the equivalent of operatorconstitutive mutations in bacterial operons.
A prophage is induced to enter the lytic cycle when the lysogenic circuit is broken. This happens when the repressor is inactivated. The absence of repressor allows RNA polymerase to bind at PL and PR , starting the lytic cycle, as shown in FIGURE 1.
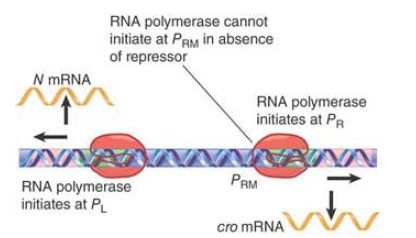
FIGURE 1. In the absence of repressor, RNA polymerase initiates at the left and right promoters. It cannot initiate at PRM in the absence of repressor.
The autoregulatory nature of the repressor maintenance circuit creates a sensitive response. The presence of the lambda repressor is necessary for its own synthesis; therefore, expression of the cI gene stops as soon as the existing repressor is destroyed. Thus, no repressor is synthesized to replace the molecules that have been damaged. This enables the lytic cycle to start without interference from the circuit that maintains lysogeny.
The region including the left and right operators, the cI gene, and the cro gene determines the immunity of the phage. Any phage that possesses this region has the same type of immunity, because it specifies both the repressor protein and the sites on which the repressor acts. Accordingly, this is called the immunity region . Each of the four lambdoid phages ϕ80, 21, 434, and λ has a unique immunity region. When we say that a lysogenic phage confers immunity to any other phage of the same type, we mean more precisely that the immunity is to any other phage that has the same immunity region (irrespective of differences in other regions).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















