

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
The lac Repressor Binds to Three Operators and Interacts with RNA Polymerase
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
الجزء والصفحة:
4-6-2021
2779
The lac Repressor Binds to Three Operators and Interacts with RNA Polymerase
KEY CONCEPTS
- Each dimer in a repressor tetramer can bind an operator; thus, the tetramer can bind two operators simultaneously.
- Full repression requires the repressor to bind to an additional operator downstream or upstream, as well as to the primary operator at the lacZ promoter.
- Binding of repressor at the operator stimulates binding of RNA polymerase at the promoter but precludes transcription.
The repressor dimer is sufficient to bind the entire operator sequence. Why, then, is a tetramer required to establish full repression?
Each dimer can bind an operator sequence. This enables the intact tetrameric repressor to bind to two operator sites simultaneously. In fact, the initial region of the lac operon has two additional operator sites. The original operator, O1, is located just at the start of the lacZ gene. It has the strongest affinity for repressor. Weaker operator sequences are located on either side; O2 is 410 bp downstream of the start point in lacZ and O3 is 88 bp upstream of lacO1, within the lacI gene.
FIGURE 1. predicts what happens when a DNA-binding protein simultaneously binds to two separated sites on DNA. The DNA between the two sites forms a loop from a base where the protein has bound the two sites. The length of the loop depends on the distance between the two binding sites. When the lac repressor binds simultaneously to O1 and to one of the other operators, it causes the DNA between them to form a rather short loop, significantly constraining the DNA structure. A scale model for binding of tetrameric repressor to two operators is shown in FIGURE 2. Low-resolution, looped complexes have been directly visualized with single-molecule experiments.
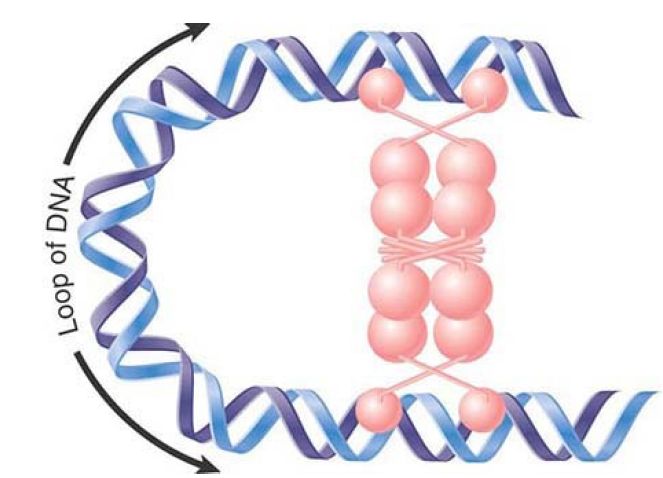
FIGURE 1. If both dimers in a repressor tetramer bind to DNA, the DNA between the two binding sites is held in a loop.
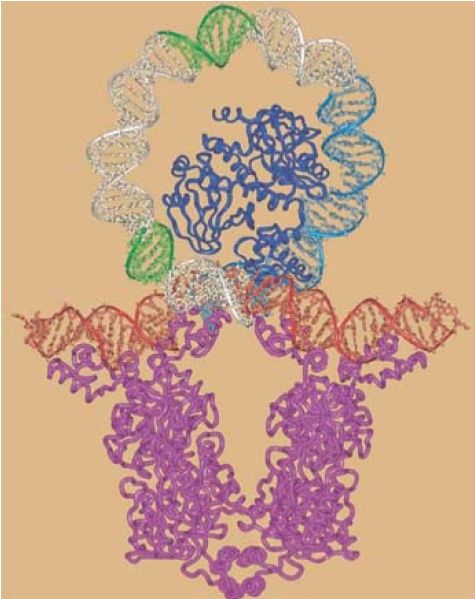
FIGURE 2. When a repressor tetramer binds to two operators, the stretch of DNA between them is forced into a tight loop. (The blue structure in the center of the looped DNA represents CRP, which is another regulator protein that binds in this region.)
Reproduced from M. Lewis et al., Science 271 (1996): 1247–1254
[http://www.sciencemag.org]. Reprinted with permission from AAAS. Photo courtesy of
Ponzy Lu, University of Pennsylvania.
Binding at the additional operators affects the level of repression. Elimination of either the downstream operator (O2) or the upstream operator (O3) reduces the efficiency of repression by two to four times. If, however, both O2 and O3 are eliminated, repression is reduced more than 50 times. This suggests that the ability of the repressor to bind to one of the two other operators, as well as to O1, is important for establishing strong repression.
In vitro experiments with supercoiled plasmids containing multiple operators demonstrate significant stabilization of the LacI–DNA complex. Nonetheless, these looped DNAs are released rapidly when the lac repressor binds to IPTG.
Several lines of evidence suggest how binding of the repressor to the operator (O1) inhibits transcription initiation by polymerase. It was originally thought that repressor binding would occlude RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter. It is now known that the two proteins may be bound to DNA simultaneously, and that, surprisingly, the binding of the repressor actually enhances the binding of RNA polymerase. The bound enzyme is prevented from initiating transcription, though. The repressor, in effect, causes RNA polymerase to be stored at the promoter. When the inducer is added, the repressor is released, and RNA polymerase can initiate transcription immediately. The overall effect of the repressor is to speed up the induction process.
Does this model apply to other systems? The interaction between RNA polymerase, the repressor, and the promoter/operator region is distinct in each system, because the operator does not always overlap with the same region of the promoter (this can be seen later in Figure 3). For example, in phage lambda, the operator lies in the upstream region of the promoter, and binding of the lambda repressor occludes the binding of RNA polymerase (see the Phage Strategies chapter). Thus, a bound repressor does not interact with RNA polymerase in the same way in all systems.
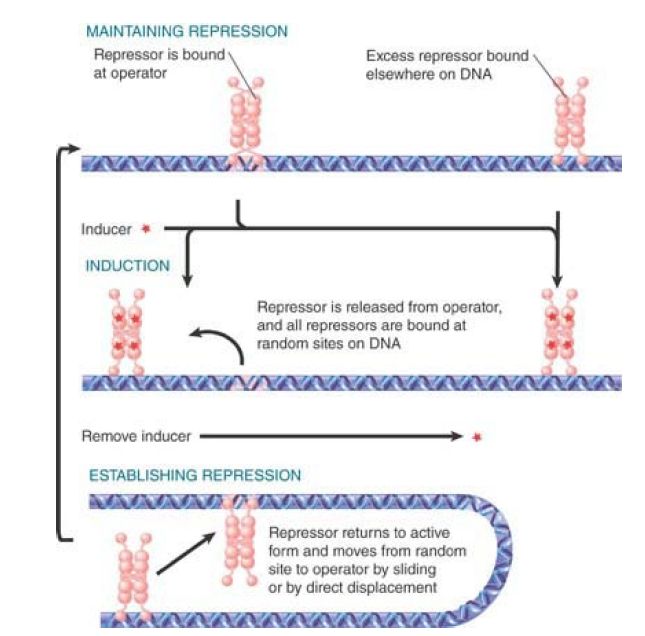
FIGURE 3. Virtually all the repressor in the cell is bound to DNA.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















