

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
SHM Is Mediated by AID, Ung, Elements of the Mismatch DNA Repair Machinery, and Translesion DNA Synthesis Polymerases
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
الجزء والصفحة:
30-4-2021
2086
SHM Is Mediated by AID, Ung, Elements of the Mismatch DNA Repair Machinery, and Translesion DNA Synthesis Polymerases
KEY CONCEPTS
- Somatic hypermutation (SHM) uses some of the same critical elements of class switch recombination (CSR).Like CSR, SHM requires activation-induced deaminase (AID).
- Ung intervention influences the pattern of somatic
mutations.
- Elements of the mismatch repair (MMR) pathway and TLS DNA polymerases are involved in SHM and CSR.
The deamination or removal of a deoxycytosine base leads to insertion of somatic mutation(s) in different ways (FIGURE 1). When AID deaminates a deoxycytosine, it gives rise to deoxyuridine. This is not germane to DNA and can be dealt with by the B cell in different ways. The deoxyuridine can be “replicated over”; it will pair with deoxyadenine during replication. The emerging mutation is an obligatory dC → dT transition and dG →dA transition on the complementary strand. The net result is the replacement of the original dC-dG pair with a dT-dA pair in half of the progeny cells. Alternatively, the deoxyuridine can be removed from DNA by Ung to give rise to an abasic site. Indeed, the key event in generating a random spectrum of mutations is the creation of an abasic site. This can be replicated over by an error-prone TLS DNA polymerase, such as polymerase ζ, polymerase η, or polymerase θ, which can insert all three possible mismatches (mutations) across the abasic site . In another mechanism, the dU-dG mispair recruits the MMR machinery, starting with Msh2/Msh6, to excise the stretch of DNA containing the damage, thereby creating a gap that needs to be filled in by resynthesis of the missing DNA strand (see the section Controlling the Direction of Mismatch Repair in the Repair Systems chapter). This resynthesis is carried out by an error-prone TLS polymerase, which will introduce mutations. What restricts the activity of the SHM machinery to only target V(D)J regions is still unknown. Ung can be blocked by introducing into cells the bacteriophage PSB-2 gene encoding the uracil-DNA glycosylase inhibitor (UGI) protein. When the UGI gene is expressed in a lymphocyte cell line or Ung is knocked out, the pattern of mutations changes dramatically, with almost all mutations from dC-dG pairs comprising the predicted transition from dC-dG to dA-dT.
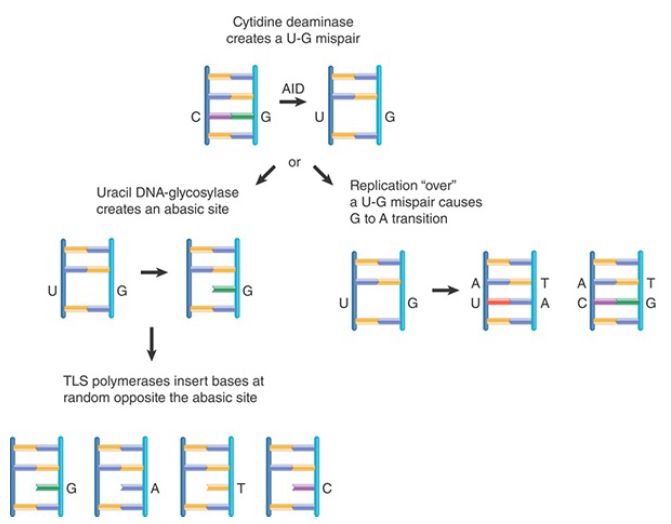
FIGURE 1. Deamination of C by AID gives rise to a U-G mispair. U can be replicated over, resulting in C-G to A-T transitions in 50% of progeny B cells. When the action of cytidine deaminase (top) is followed by that of uracil-DNA glycosylase, an abasic site is created. Replication past this site should insert all four bases at random into the daughter strand (center). If the uracil is not removed from the DNA, its replication gives rise to a C-G to T-A transition. Alternatively, the U-G mispair is recognized by the MMR machinery, which excises DNA containing the mismatch and then fills in the resulting gap using an error-prone DNA polymerase. This will lead to insertion of further mismatches (mutations).
The main difference between CSR and SHM is the nature of DNA lesions underpinning the two processes. DSBs are introduced as obligatory intermediates in CSR, whereas individual point mutations are introduced as events of single-strand cleavages in SHM. AID and/or DNA repair factor(s) also function as scaffolds to assemble different protein complexes in CSR and SHM. Thus, AID and DNA repair factors contribute to these processes through both enzymatic and nonenzymatic functions, possibly in different ways.
AID plays a central role in both CSR and SHM. However, whereas Ung intervention is a central event in CSR, it is not necessarily in SHM, and TLS polymerases play a greater role in SHM than CSR.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















