
Recombination Is an Important Mechanism to Recover from Replication Errors
 المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
 المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 20-4-2021
20-4-2021
 2040
2040
Recombination Is an Important Mechanism to Recover from Replication Errors
KEY CONCEPTS
- A replication fork may stall when it encounters a damaged site or a nick in DNA.
- A stalled fork may reverse by pairing between the two newly synthesized strands.
- A stalled fork may restart after repairing the damage and use a helicase to move the fork forward.
- The structure of the stalled fork is the same as a Holliday junction and may be converted to a duplex and doublestrand break by resolvases.
In many cases, rather than skipping a DNA lesion, DNA polymerase instead stops replicating when it encounters DNA damage. FIGURE 1. shows one possible outcome when a replication fork stalls. The fork stops moving forward when it encounters the damage.
The replication apparatus disassembles, at least partially. This allows branch migration to occur, when the fork effectively moves backward, and the new daughter strands pair to form a duplex structure. After the damage has been repaired, a helicase rolls the fork forward to restore its structure. Then the replication apparatus can reassemble, and replication is restarted .
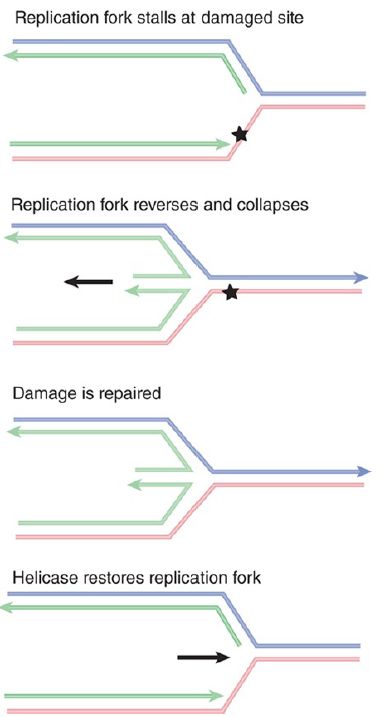
FIGURE 1. A replication fork stalls when it reaches a damaged site in DNA. Reversing the fork allows the two daughter strands to pair. After the damage has been repaired, the fork is restored by forward-branch migration catalyzed by a helicase. Arrowheads indicate 3’ ends.
The pathway for handling a stalled replication fork requires repair enzymes, and restarting stalled replication forks is thought to be a major role of the recombination-repair systems. In E. coli, the RecA and RecBC systems have an important role in this reaction (in fact, this may be their major function in the bacterium). One possible pathway is for RecA to stabilize single-stranded DNA by binding to it at the stalled replication fork and possibly acting as the sensor that detects the stalling event. RecBC is involved in excision repair of the damage. After the damage has been repaired, replication can resume.
Another pathway may use recombination-repair—possibly the strand-exchange reactions of RecA. FIGURE 2. shows that the structure of the stalled fork is essentially the same as a Holliday junction created by recombination between two duplex DNAs . This makes it a target for resolvases. A DSB is generated if a resolvase cleaves either pair of complementary strands. In addition, if the damage is in fact a nick, another DSB is created at this site.
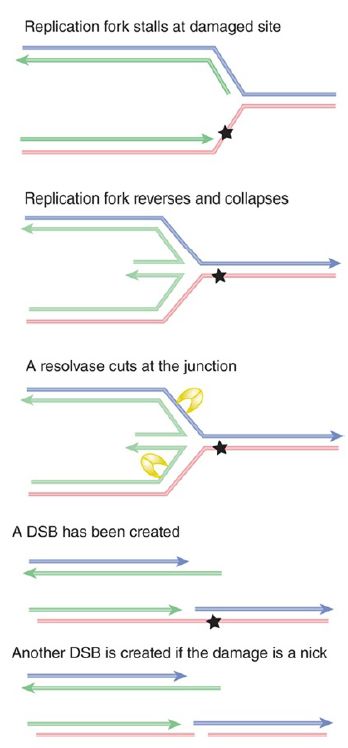
FIGURE 2. The structure of a stalled replication fork resembles a Holliday junction and can be resolved in the same way by resolvases. The results depend on whether the site of damage contains a nick. Result 1 shows that a double-strand break is generated by cutting a pair of strands at the junction. Result 2 shows that a second double-strand break is generated at the site of damage if it contains a nick. Arrowheads indicate 3’ ends.
Stalled replication forks can be rescued by recombination-repair events. Although the exact sequence of events is not yet known, one possible scenario is outlined in FIGURE 3. The principle is that a recombination event occurs on either side of the damaged site, allowing an undamaged single strand to pair with the damaged strand. This allows the replication fork to be reconstructed so that replication can continue, effectively bypassing the damaged site.
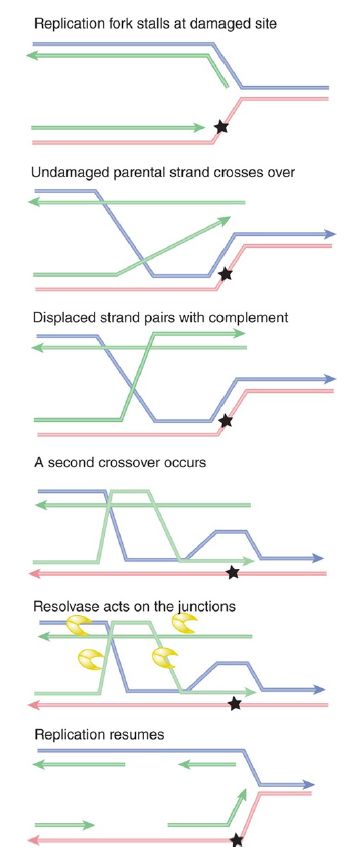
FIGURE 3. When a replication fork stalls, recombination-repair can place an undamaged strand opposite the damaged site. This allows replication to continue.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


