

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
DNA Polymerase Holoenzyme Consists of Subcomplexes
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
الجزء والصفحة:
5-4-2021
2743
DNA Polymerase Holoenzyme Consists of Subcomplexes
KEY CONCEPTS
- The E. coli DNA polymerase III catalytic core contains three subunits, including a catalytic subunit and a proofreading subunit.
- The DNA Pol III holoenzyme has at least two catalytic cores, a processivity clamp, and a dimerization clamploader complex.
- A clamp loader places the processivity subunits on DNA,where they form a circular clamp around the nucleic acid.
- At least one catalytic core is associated with each template strand.
- The E. coli replisome is composed of the holoenzyme complex and the additional enzymes required for chromosome replication.
We can now relate the subunit structure of E. coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme (also called a replisome) to the activities required for DNA synthesis and propose a model for its action. The replisome consists of the DNA polymerase III holoenzyme complex and associated proteins, primase and helicase, necessary for replication function. A new model for the structure of the DNA Pol III complex proposes a three-polymerase core structure, with two Pol III catalytic cores responsible for synthesis of the lagging strand and one for the leading strand. Each Okazaki fragment is synthesized by a new alternating core polymerase. The holoenzyme is a complex of 900 kD that contains 10 different proteins organized into four types of subcomplex:
- There are at least two copies of the catalytic core. Each catalytic core contains the α subunit (the DNA polymerase activity), the ε subunit (the 3′–5′ proofreading exonuclease), and the θ subunit (which stimulates the exonuclease).
- There are two copies of the dimerizing subunit, τ, which link the two catalytic cores together.
There are two copies of the clamp, which is responsible for holding catalytic cores onto their template strands. Each clamp consists of a homodimer of β subunits, the β ring, which binds around the DNA and ensures processivity.
- The γ complex is a group of seven proteins, encoded by five genes that comprise the clamp loader; the clamp loader places the β clamp on DNA by opening the ring.
FIGURE 1 shows one of the models for the assembly of DNA polymerase III. The holoenzyme assembles on DNA in three stages:
- First, the clamp loader uses hydrolysis of ATP to bind β subunits to a template-primer complex.
- Binding to DNA changes the conformation of the site on β that binds to the clamp loader, and as a result it now has a high affinity for the core polymerase. This enables core polymerase to bind, and this is the means by which the core polymerase is brought to DNA.
- A τ dimer binds to the core polymerase and provides a dimerization function that binds a second core polymerase (associated with another β2 clamp). The replisome is an asymmetric dimer because it has only one clamp loader and (at least) two copies of the catalytic core. The clamp loader is responsible for adding a pair of β2 dimers to each parental strand of DNA.
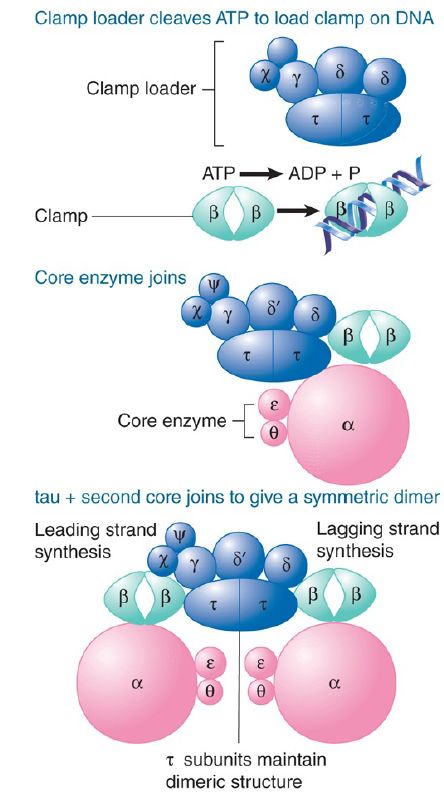
FIGURE 1. DNA polymerase III holoenzyme assembles in stages, generating an enzyme complex that synthesizes the DNA of both new strands.
Each of the core complexes of the holoenzyme synthesizes one of the new strands of DNA. The clamp loader is also needed for unloading the β clamp from DNA; as a result, the two cores have different abilities to dissociate from DNA. This corresponds to the need to synthesize a continuous leading strand (where polymerase remains associated with the template) and a discontinuous lagging strand (where polymerase repetitively dissociates and reassociates). The clamp loader is associated with the core polymerase that synthesizes the lagging strand and plays a key role in the ability to synthesize individual Okazaki fragments.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















