
Quantitative or Real-time PCR
 المؤلف:
John M Walker and Ralph Rapley
المؤلف:
John M Walker and Ralph Rapley
 المصدر:
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 5th Edition
المصدر:
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 5th Edition
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 18-11-2020
18-11-2020
 2356
2356
Quantitative or Real-time PCR
Another useful PCR development is quantitative PCR (Q-PCR) or realtime PCR (confusingly also referred to as RT-PCR). Quantitative PCR is suited to many applications because of the rapidity of the method compared with conventional PCR, while simultaneously providing a lower limit of detection and greater dynamic range. Another advantage is that Q-PCR permits a rigorous analysis of PCR problems as they arise. Early quantitative PCR methods involved the comparison of a standard or control DNA template amplified with separate primers at the same time as the specific target DNA.These types of quantification rely on the reaction being exponential and so any factors affecting this may also affect the result. Other methods involve the incorporation of a radiolabel through the primers or nucleotides and their subsequent detection following purification of the amplicon. An alternative automated real-time PCR method is the 50 fluorogenic exonuclease detection system or TaqMan.In its simplest form, a DNA-binding dye such as SYBR Green is included in the reaction. As amplicons accumulate, SYBR Green binds the dsDNA proportionally. Fluorescence emission of the dye is detected following excitation. The binding of SYBR Green is non-specific. Therefore, in order to detect specific amplicons, an oligonucleotide probe labelled with a fluorescent reporter and quencher molecule at either end is included in the reaction in the place of SYBR Green. When the oligonucleotide probe binds to the target sequence, the 5´ exonuclease activity of Taq polymerase degrades and releases the reporter from the quencher (Figure 5.8). A signal is generated which increases in direct proportion to the number of starting molecules.
Hence the detection system is able to induce and detect fluorescence in real time as the PCR proceeds. In addition to quantification of the reaction, real-time PCR may also be used for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms and for accurate determination of amplicon melting temperature using curve analysis. Other probe-based PCR systems have been devised, such as the use of scorpion probes.
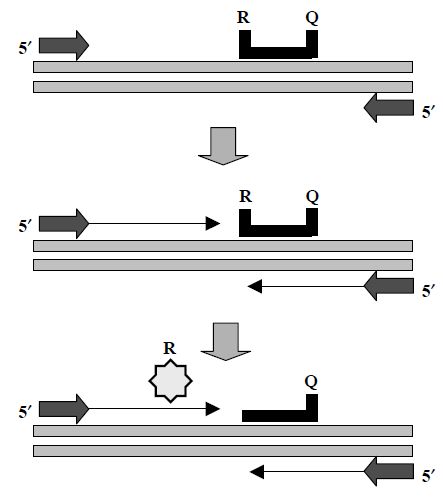
Figure 5.8 The 5´ nuclease assay (TaqMan) employs a standard PCR together with a small oligonucleotide probe. The probe is labelled with a fluorescent reporter (R) at one and a quencher (Q) at the other. The close proximity of the R–Q quenches fluorescence. The R–Q probe binds to its complementary PCR fragment until cleaved by the 5´ nuclease activity of Taq polymerase. Once the R group is released an increase in fluorescence is detected. Thus the performance of the PCR is measured in real time.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


