
X-ray astronomy: X-ray spectrometry
 المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
 المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 385
الجزء والصفحة:
p 385
 2-9-2020
2-9-2020
 1981
1981
X-ray astronomy: X-ray spectrometry
X-ray spectrometry or energy isolation can also be performed by using the crystal planes of materials to act in the same way as a diffraction grating for the optical spectrum, the principle being that of the Bragg spectrometer as sketched in figure 1. Interference is achieved according to the dimensions of the lattice and the wavelengths of the incident x-rays.
Some of the incident radiation is scattered by the first layer of the crystal lattice—radiation penetrating the crystal is scattered by successive layers. It can be readily seen from figure 1 that the path difference for the radiation emerging from two adjacent layers is 2d sin θg where d is the crystal plane separation and θg is the grazing angle.
For constructive interference to occur, the path lengths need to be equal to an integer number of wavelengths, that is
mλ = 2d sin θg
where m is an integer. The spectrum can, therefore, be readily scanned by altering the angle of θg by
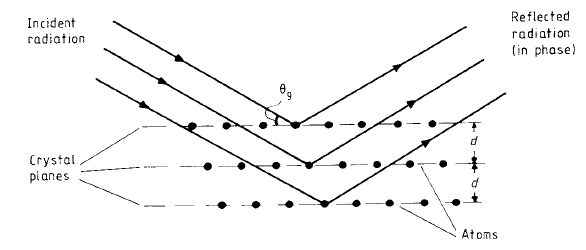
Figure 1. The principle of the Bragg spectrometer for x-rays.
rotation of the crystal surface. Materials used as ‘gratings’ are lithium fluoride, tungsten disulphide and graphite.
As will emerge in the following subsection, some x-ray detectors themselves allow the energy of each photon to be determined.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


