
Reflectors: Cassegrain reflectors
 المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
 المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 260
الجزء والصفحة:
p 260
 21-8-2020
21-8-2020
 2482
2482
Reflectors: Cassegrain reflectors
The Cassegrain normally consists of a large spherical or paraboloidal primary mirror with a secondary mirror which is complex or hyperboloidal. The optical arrangement is illustrated in figure 1, from which it can be seen that not only is the central portion of the primary mirror not used but it is also machined out to allow the converging beam to be brought to focus behind the primary mirror. It can also be seen that the effective focal length of the system is increased by the secondary mirror.

Figure 1. The Cassegrain system.
If Fp is the focal length of the primary mirror (a positive value), Fs the focal length of the secondary mirror (a
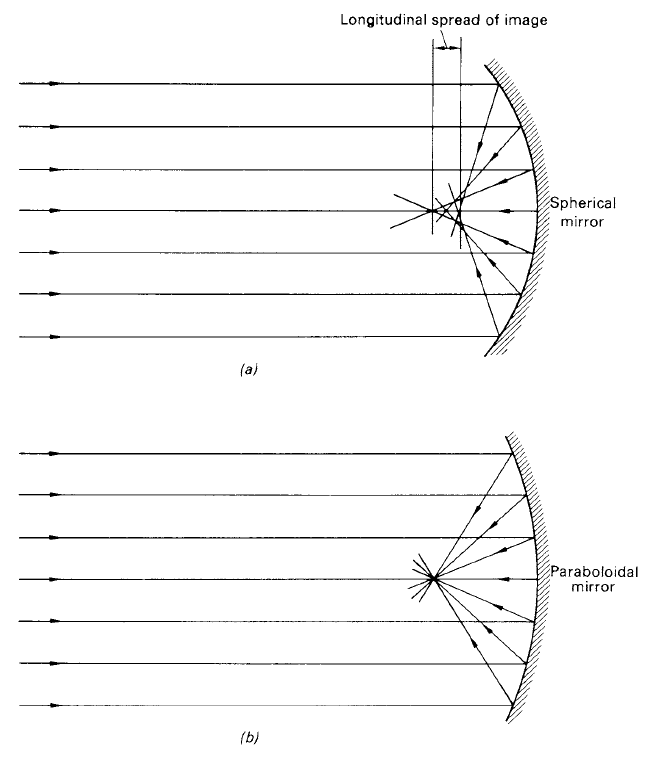
Figure 2. (a) Spherical mirror exhibiting the effect of spherical aberration. (b) Paraboloidal mirror removes spherical aberration; incident rays parallel to the optic axis are brought to the same focus, independent of their distance from the axis.
negative value) and if the secondary is placed at a distance d inside the focus of the primary mirror, the resulting focus will be found in the plane of the primary mirror when
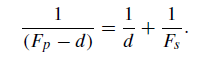 (1)
(1)
The equivalent focal length of the combination (defined as the focal length of a single imaging device which would provide the same size of image in its focal plane) is given by the focal length of the primary mirror multiplied by the magnification provided by the secondary mirror. If the equivalent focal length is denoted by Fe, then
 (2)
(2)
For typical Cassegrain telescopes, the value of the magnification (Fp − d)/d by the secondary mirror lies somewhere between two and five, according to the individual design. The secondary mirror must be sufficiently large to accept all the light of the convergent cone from the primary. The diameter needed and hence the fraction of the central part of the primary mirror which is not used, depends on the magnification of the secondary mirror. Some small adjustment of the position of the secondary mirror is usually made available by push-button control and the position of the final focus can be altered by this means. This is particularly convenient when a range of equipment is available for fixing to the base plate of the telescope.
One of the modified forms of the Cassegrain system is known as the Ritchey–Chr´etian telescope. In this telescope, both coma and spherical aberration are removed. Astigmatism and field curvature are greatly reduced at the expense of having a larger diameter of secondary mirror than is usual for an ordinary Cassegrain telescope. Thus, although the light-grasp is not as great as the same size of Cassegrain telescope, the image quality is greatly improved.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


