
Laguerre Differential Equation
 المؤلف:
Iyanaga, S. and Kawada, Y.
المؤلف:
Iyanaga, S. and Kawada, Y.
 المصدر:
Encyclopedic Dictionary of Mathematics. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press
المصدر:
Encyclopedic Dictionary of Mathematics. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press
 الجزء والصفحة:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
 13-6-2018
13-6-2018
 1392
1392
Laguerre Differential Equation
The Laguerre differential equation is given by
 |
(1)
|
Equation (1) is a special case of the more general associated Laguerre differential equation, defined by
 |
(2)
|
where  and
and  are real numbers (Iyanaga and Kawada 1980, p. 1481; Zwillinger 1997, p. 124) with
are real numbers (Iyanaga and Kawada 1980, p. 1481; Zwillinger 1997, p. 124) with  .
.
The general solution to the associated equation (2) is
 |
(3)
|
where  is a confluent hypergeometric function of the first kind and
is a confluent hypergeometric function of the first kind and  is a generalized Laguerre polynomial.
is a generalized Laguerre polynomial.
Note that in the special case  , the associated Laguerre differential equation is of the form
, the associated Laguerre differential equation is of the form
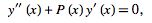 |
(4)
|
so the solution can be found using an integrating factor
as
where  is the En-function.
is the En-function.
The associated Laguerre differential equation has a regular singular point at 0 and an irregular singularity at  . It can be solved using a series expansion,
. It can be solved using a series expansion,
 |
(12)
|
 |
(13)
|
 |
(14)
|
![[(nu+1)a_1+lambdaa_0]+sum_(n=1)^(infty)<span style=]() {[(n+1)n+(nu+1)(n+1)]a_(n+1)-na_n+lambdaa_n}x^n=0 " src="http://mathworld.wolfram.com/images/equations/LaguerreDifferentialEquation/Inline33.gif" style="height:44px; width:441px" /> {[(n+1)n+(nu+1)(n+1)]a_(n+1)-na_n+lambdaa_n}x^n=0 " src="http://mathworld.wolfram.com/images/equations/LaguerreDifferentialEquation/Inline33.gif" style="height:44px; width:441px" /> |
(15)
|
![[(nu+1)a_1+lambdaa_0]+sum_(n=1)^(infty)[(n+1)(n+nu+1)a_(n+1)+(lambda-n)a_n]x^n=0.](http://mathworld.wolfram.com/images/equations/LaguerreDifferentialEquation/Inline34.gif) |
(16)
|
This requires
for  . Therefore,
. Therefore,
 |
(19)
|
for  , 2, ..., so
, 2, ..., so
If  is a nonnegative integer, then the series terminates and the solution is given by
is a nonnegative integer, then the series terminates and the solution is given by
 |
(23)
|
where  is an associated Laguerre polynomial and
is an associated Laguerre polynomial and  is a Pochhammer symbol. In the special case
is a Pochhammer symbol. In the special case  , the associated Laguerre polynomial collapses to a usual Laguerre polynomial and the solution collapses to
, the associated Laguerre polynomial collapses to a usual Laguerre polynomial and the solution collapses to
 |
(24)
|
REFERENCES:
Iyanaga, S. and Kawada, Y. (Eds.). Encyclopedic Dictionary of Mathematics. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, p. 1481, 1980.
Zwillinger, D. Handbook of Differential Equations, 3rd ed. Boston, MA: Academic Press, p. 120, 1997.
 الاكثر قراءة في معادلات تفاضلية
الاكثر قراءة في معادلات تفاضلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


