


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 15-11-2020
Date: 1-1-2016
Date: 6-12-2015
|
EDTA (Ethylenediamine-N,N,N′,N′-Tetraacetic Acid(
EDTA is a chelating agent widely used, along with EGTA, to control the concentration of divalent and trivalent cations in aqueous solutions. Its structure is given in Figure 1. It is an essential ingredient in such diverse products as laundry detergents and film developers. In the field of molecular biology, EDTA is present in many buffer solutions used for experiments where the presence of divalent and trivalent cations would interfere with the desired outcome. For example, it is used in most buffers for the initial steps of protein purification (1) from biological material, to suppress the activity of metal-dependent proteases that would otherwise degrade the desired protein.

Figure 1. Chemical structure of EDTA (ethylenediamine- N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid).
The flexibility of the molecule, and the variety of potential liganding sites within it, permit EDTA to accommodate a wide variety of cation types, preferred ligand geometries and bond lengths, thus contributing to its high affinity for most cations (Table 1) (2). In contrast to many other complexing agents, EDTA will form only a 1:1 complex with either divalent and trivalent cations, in which a single ion is chelated by all four carboxyl groups, which greatly contributes to the stability of the resulting complex. Hence, EDTA can maintain the concentration of free cations at very low levels. The high affinity of EDTA for cations is also used to removed metals from metalloproteins and to maintain them in their metal-free state. It is important to note that the binding of cations by EDTA is
pH-dependent; protonation of the carboxylate moieties at low pH dramatically lowers their affinity for cations.
Table 1. Affinity of EDTA for Various Cations a
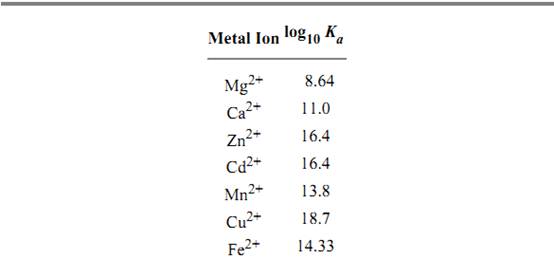

a The logarithm of the association constant [Ka in units of M–1 (reciprocal molars)] are compared at pH 7.0, 25°C, and 0.1 M ionic strength (2).
EDTA as the free acid is a white powder, has a molecular weight of 292.25 Da, decomposes at 240°C, and is relatively insoluble in water (0.34 g/100 mL at 25°C). The sodium and potassium salts of EDTA are also white powders and are much more readily soluble in water.
References
1. J. E. Coligan et al. (eds), Current Protocols in Protein Science John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, U.K. (1995).
2. A. E. Martell and R. M. Smith (1974) Critical Stability Constants Vol. 1, Plenum Press, New York.



|
|
|
|
صنع الذكريات والتفكير يدمر الدماغ.. دراسة تشرح السبب
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الصين.. عودة كاسحتي الجليد إلى شنغهاي بعد انتهاء بعثة استكشافية إلى القطب الجنوبي
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تكرم الفائزين بأبحاث طلبة كلية الصيدلة وطب الأسنان
|
|
|
|
مشروع التكليف الشرعي بنسخته السادسة الورود الفاطمية... أضخم حفل لفتيات كربلاء
|
|
|
|
ضمن جناح جمعيّة العميد العلميّة والفكريّة المجمع العلمي يعرض إصداراته في معرض تونس الدولي للكتاب
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تعقد مؤتمرها الطلابي العلمي الرابع
|