


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 23-3-2021
Date: 9-5-2017
Date: 28-3-2021
|
The Infinite Potential Well
The problem of a particle in the infinite potential well is a classic example of a bound particle. The potential V(x) as a function of position for this problem is shown in

Figure 1.1 Potential function of the infinite potential well.
Figure 1.1. The particle is assumed to exist in region I1 so the particle is contained within a finite region of space. The time-independent Schrodinger's wave equation is again given by Equation (1) as
 (1)
(1)
where E is the total energy of the particle. If E is finite, the wave function must be zero, or ѱ(x) = 0, in both regions I and III. A particle cannot penetrate these infinite potential barriers, so the probability of finding the particle in regions I and III is zero.
The time-independent Schrodinger's wave equation in region II, where V = 0. Becomes
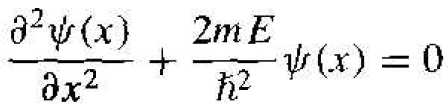 (2)
(2)
A particular form of solution to this equation 1s given by
 (3)
(3)
where
 (4)
(4)
One boundary condition is that the wave function ѱ(x) must be continuous so that
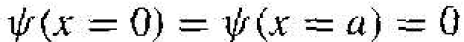 (5)
(5)
Applying the boundary condition at x = 0, we must have that A1 = 0. At x = a, we have
 (6)
(6)
This equation is valid if Ka = nπ. where the parameter n is a positive integer, or n = 1,2,3. . . . . The parameter n is referred to as a quantum number. We can write
 (7)
(7)
Negative values of n simply introduce a negative sign in the wave function and yield redundant solutions for the probability density function. Wc cannot physically distinguish any difference between +n and -n solutions. Because of this redundancy, negative values of n are not considered.
The coefficient A2 can be found from the normalization boundary condition that was give as 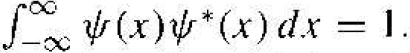 If we assume that the wave function solution ѱ(x) is a real function, then ѱ(x) = ѱ*(x). We have
If we assume that the wave function solution ѱ(x) is a real function, then ѱ(x) = ѱ*(x). We have
 (8)
(8)
Evaluating this integral gives
 (9)
(9)
Finally. the time-independent wave solution is given by
 (10)
(10)
This solution represents the electron in the infinite potential well and is a standing wave solution. The free electron was represented by a traveling wave. and now the bound particle is represented by a standing wave.
The parameter K in the wave solution was defined by Equations (4) and (7). Equating these two expressions for K. we obtain
 (11)
(11)
The total energy can then be written as
 (12)
(12)
For the particle in the infinite potential well. the wave function is now given by
 (13)
(13)
where the constant K must have discrete values, implying that the total energy of the particle can only have discrete values. This result means that the energy of the particle is quantized. That is, the energy of the particle can only have particular discrete values. The quantization of the particle energy is contrary to results from classical physics, which would allow the particle to have continuous energy values. The discrete energies lead to quantum states that will be considered in more detail in this and later chapters. The quantization of the energy of a bound particle is an extremely important result.



|
|
|
|
حمية العقل.. نظام صحي لإطالة شباب دماغك
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
إيرباص تكشف عن نموذج تجريبي من نصف طائرة ونصف هليكوبتر
|
|
|
|
|
|
اختتام الأسبوع الثاني من الشهر الثالث للبرنامج المركزي لمنتسبي العتبة العباسية
|
|
|
|
راية قبة مرقد أبي الفضل العباس (عليه السلام) تتوسط جناح العتبة العباسية في معرض طهران
|
|
|
|
جامعة العميد وقسم الشؤون الفكرية يعقدان شراكة علمية حول مجلة (تسليم)
|
|
|
|
قسم الشؤون الفكريّة يفتتح باب التسجيل في دورات المواهب
|